Fatty liver is a growing health concern that affects millions of people around the world. It’s a condition caused by excessive fat buildup in the liver, resulting in inflammation and scarring. But can fatty liver be reversed? The answer is yes–but it depends on how far along the disease has progressed. In this blog post, we’ll explore the stages of fatty liver disease (known as NAFLD and NASH) and what treatments are available to reverse it. We also discuss lifestyle changes you can make to help manage your condition and improve your overall health.
What is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver. This can be caused by many things, including obesity, diabetes, and drinking too much alcohol. Fatty liver can lead to serious health problems, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Most people with fatty liver have no symptoms. However, some people may develop fatigue, pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, or yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
Fatty liver is often diagnosed with blood tests and imaging tests, such as ultrasound. Treatment for fatty liver typically focuses on lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. Certain herbs for fatty liver can also be used to assist in healing and cleansing your liver.. In some cases, medication may be needed to help manage fatty liver especially if you had your gallbladder removed..

How is Fatty Liver diagnosed?
There are a few different ways that fatty liver can be diagnosed. One way is through a physical exam. Your doctor may be able to see or feel an enlarged liver if you have fatty liver.
Another way to diagnose fatty liver is through blood tests. These tests can show elevated levels of certain enzymes that are released when the liver is damaged.
Imaging tests, such as ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs, can also be used to diagnose fatty liver. These tests can show the amount of fat in your liver and whether there is any scarring present.
If you are suspected of having fatty liver, your doctor may recommend a biopsy. This is a procedure where a small sample of tissue is taken from your Liver and examined under a microscope. A biopsy can confirm the diagnosis of fatty liver and help determine the severity of the condition.
Can Fatty Liver be reversed?
Yes, fatty liver can be reversed. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are both reversible.
If you have NAFLD, you may be able to reverse it by losing weight and exercising more. If you have NASH, you may need to take medication to reduce the fat in your liver.
How to know if you have fatty liver?
If you have fatty liver, it means that there is an excessive amount of fat in your liver. This can be caused by many things, including obesity, diabetes, and drinking too much alcohol. Fatty liver is a serious condition that can lead to cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) and liver failure. There are two types of fatty liver: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD). NAFLD is the most common type of fatty liver and usually affects people who are obese or have diabetes. AFLD occurs when there is too much alcohol in the liver. If you think you may have either type of fatty liver, it is important to see your doctor right away so that you can get treated.
Causes of Fatty Liver
There are many possible causes of fatty liver, including obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and high triglycerides. Other possible causes include alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and certain medications. In most cases, the exact cause is unknown.
Obesity is the most common cause of fatty liver in the United States. Obesity can lead to insulin resistance, which is a major factor in the development of NASH. Diabetes is also a risk factor for NASH. People with diabetes have an increased risk of developing fatty liver because they are more likely to have high levels of triglycerides and low levels of HDL (good) cholesterol.
High cholesterol and high triglycerides are also risk factors for fatty liver. Triglycerides are a type of fat that circulates in the blood. High levels of triglycerides can damage the liver and lead to inflammation. HDL cholesterol helps remove triglycerides from the blood. People with low HDL levels are at increased risk for developing fatty liver.
Alcohol abuse is another possible cause of fatty liver. Alcohol abuse can lead to steatosis, which is an accumulation of fat in the liver. Steatohepatitis is a type of steatosis that also includes inflammation of the liver. Alcoholic hepatitis is a more severe form of alcoholic steatohepatitis that can be life-threatening.
Viral hepatitis is another possible cause of fatty liver. Hepatitis C is the most common type of viral hepatitis in the United States and it can result in serious, even life-threatening health problems like cirrhosis and liver cancer.

Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver. It can be caused by many things, including alcohol abuse, obesity, and diabetes. Fatty liver can lead to serious health problems, including cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) and liver cancer.
There are often no symptoms of fatty liver. When symptoms do occur, they may include fatigue, weight loss, nausea, and pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. If you have any of these symptoms, see your doctor. They can do tests to check for fatty liver.
Treatment for fatty liver usually involves lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. If you have fatty liver due to alcohol abuse, you will need to stop drinking alcohol completely.
Complications of Fatty Liver
There are a number of potential complications associated with fatty liver, including steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. NASH is a more severe form of fatty liver disease that can lead to inflammation and scarring of the liver. Fibrosis is the buildup of scar tissue in the liver, and cirrhosis is the late stage of fibrosis in which the liver is significantly damaged. Liver cancer is a rare but serious complication of fatty liver disease.
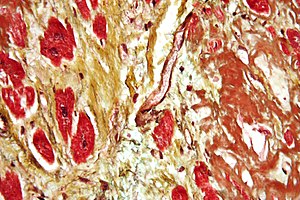
If you have fatty liver disease, it is important to be aware of these potential complications and to see your doctor regularly for monitoring. Treatment for fatty liver disease may help to prevent or delay the development of these complications.
Treatments for Fatty Liver
There are two main types of fatty liver: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NAFLD is the most common type of fatty liver. It happens when fat builds up in your liver, even if you don’t drink much alcohol. NASH is a more serious form of NAFLD. It happens when fat, inflammation and cell damage cause scarring in your liver. NASH can lead to cirrhosis or permanent damage to your liver.
The good news is that fatty liver can be reversed. Losing weight is the best way to treat both NAFLD and NASH. If you’re overweight or obese, losing 5% to 10% of your body weight can improve your fatty liver. If you have NASH, you may need to lose more weight to help reduce the inflammation in your liver.
In addition to weight loss, you can treat fatty liver with:
- Exercise: Getting regular exercise can help reduce fat in your liver and improve your insulin resistance.
- Healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet can help you lose weight and reduce the fat in your liver. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbs. Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats.
- Medications: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medications to help treat fatty liver. These include metformin
Diet for Fatty Liver
There is no one-size-fits-all diet for fatty liver, but there are some general guidelines that may help.
- First, it is important to eat a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of alcohol.
- Second, make sure you are getting enough fiber. Fiber helps to promote healthy digestion and can also help to reduce the amount of fat that is absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Third, limit your intake of saturated fats and trans fats. These types of fats can contribute to the development of fatty liver disease. Instead, focus on eating healthy fats such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
- Fourth, if you are overweight or obese, lose weight gradually through a healthy diet and exercise program. Losing weight too quickly can actually worsen fatty liver disease.
- Finally, avoid crash diets or fad diets that promise quick weight loss. These types of diets are often unhealthy and can actually lead to long-term weight gain.

Prevention of Fatty Liver
In order to prevent fatty liver, it is important to maintain a healthy weight and avoid obesity. It is also important to eat a healthy diet that is low in fat and sugar. Exercise regularly and avoid excessive alcohol consumption. If you have diabetes, it is important to control your blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fatty liver disease can be reversed with the right lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise. It is important to keep in mind that more serious forms of fatty liver, such as NASH and NAFLD, require medical attention. With proper treatment, these diseases can be managed effectively and complications avoided. If you are experiencing any symptoms related to fatty liver or think you may have it, speak to your doctor for further advice on how to manage it properly.


I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.